5 Key Steps to Effective SAP Testing

In today’s cutthroat market, organizations heavily rely on Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems to streamline their day-to-day activities, optimize resources, and boost overall efficiency. Amidst the array of ERP solutions available, SAP (System, Applications & Products in Data Processing) stands out as a comprehensive platform.
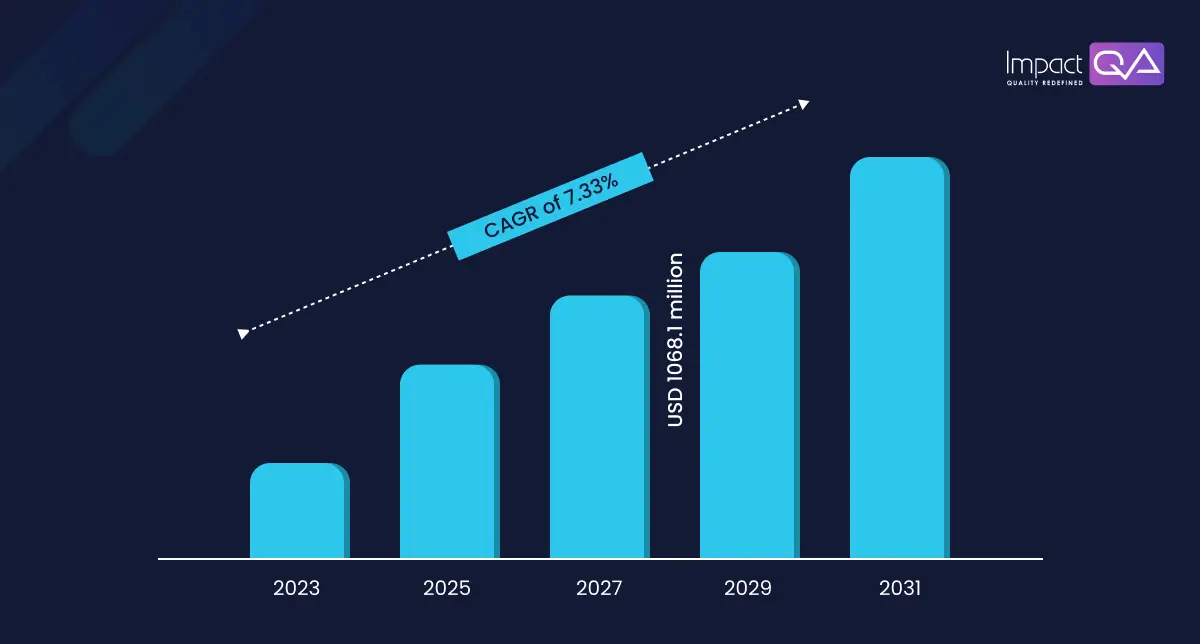
The Global SAP Testing Services market is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 7.33% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2031, reaching USD 1068.1 million by 2028. In 2024, the market is growing at a steady rate, and with the rise of the adoption of strategies by key players, the market is expected to rise above the horizon. With this rising trend, it’s crucial to understand what SAP entails and how to ensure its successful implementation through effective testing.
Effective SAP testing is crucial to ensure that all components and integrations work seamlessly, delivering a smooth user experience. By focusing on the key steps involved in the SAP testing process, organizations can maximize the benefits of their SAP systems.
What is SAP Testing?
Before delving into the key steps involved in the SAP testing process, let’s first understand what SAP testing is all about.
SAP testing is the process of verifying and validating the SAP software system throughout its Development Life Cycle (SDLC). SAP testing involves examining different modules within the SAP ERP software. A typical ERP system consists of various modules, and SAP provides a standard template for these modules, which companies then customize to meet their specific needs. After these customizations, businesses employ SAP testing service providers to ensure these adjustments function correctly and efficiently according to their standards.
Once SAP is fully integrated into a company’s system, it requires regular updates, such as new module implementations or bug fixes, which need thorough testing before being deployed. Therefore, SAP testing is an ongoing process, essential to avoid downtimes and enhance employee efficiency.
Testing Solutions for SAP Systems
There are 8 different types of SAP testing that any software testing company would incorporate into their testing suite to ensure end-to-end testing of your complete business processes.
1. Unit Testing
Unit testing involves testing every single component or isolated piece of software. More like a white-box testing technique, unit testing is generally performed by developers who have full knowledge of the complete code and programming used to test the functionality of the software. It helps reduce the cost of testing at an early stage.
2. Integration Testing
Integration Testing, like scenario testing, is generally performed with realistic data to verify the efficient functioning of systems. It ensures that integrated components work together as expected within the SAP environment. This type of testing is crucial for identifying and resolving interface issues between different modules or systems.
3. Regression Testing
Regression Testing ensures that the new changes updated in the code will not adversely affect the existing working code. SAP, being an integrated system, any change made on a single stack update, OSS note, transport note, or others can affect the functioning of the entire system in use.
4. Performance Testing
This testing checks the performance of an application under different stimuli. It examines whether the system’s response time is acceptable, what the speed of periodic processes is, whether the expected user load on the peak can be supported by the existing systems, etc. Essentially, it identifies processing bottlenecks and ABAP code inefficiencies.
5. Functional Testing
Functional Testing helps ensure that your SAP implementation meets your business requirements. SAP modules delivered by the system are highly configurable and can be easily integrated with other applications or third-party tools. Functional testing also ensures that integrations are well-executed across the platform.
6. Security Testing
Security testing ensures every user can execute transactions and have access to data that is essentially required. It’s typically done in a QA environment in which test IDs are created to give access to users as per their interaction with the software.
7. End-User Testing & User Acceptance Testing
Though closely related but not identical, the purpose of both these testing methods is to ensure the end-user can execute the designated tasks associated with that particular software. End-user and acceptance testing ideally refer to your original application blueprint. Also, check if the expected features and functions stated by the client are effectively functioning or not.
8. SAP Interface Testing
SAP Interface Testing takes place at various points throughout the project. As a part of the project development phase, isolated interface testing falls under the unit testing banner. In the QA environment, interface testing involves observing the execution of business transactions and following the business output that’s generated. Effective interface testing shows how efficiently automated your current systems are.
Key Steps to Effective SAP Testing
Transitioning to an SAP-based ERP model can be a tricky task. Agile testing for SAP systems plays a crucial role here else approaching it with a manual testing methodology can take weeks or maybe months to be fully executed. Spending too much time before you release every single time you make a change in your model means you are defeating the purpose of moving to SAP altogether.
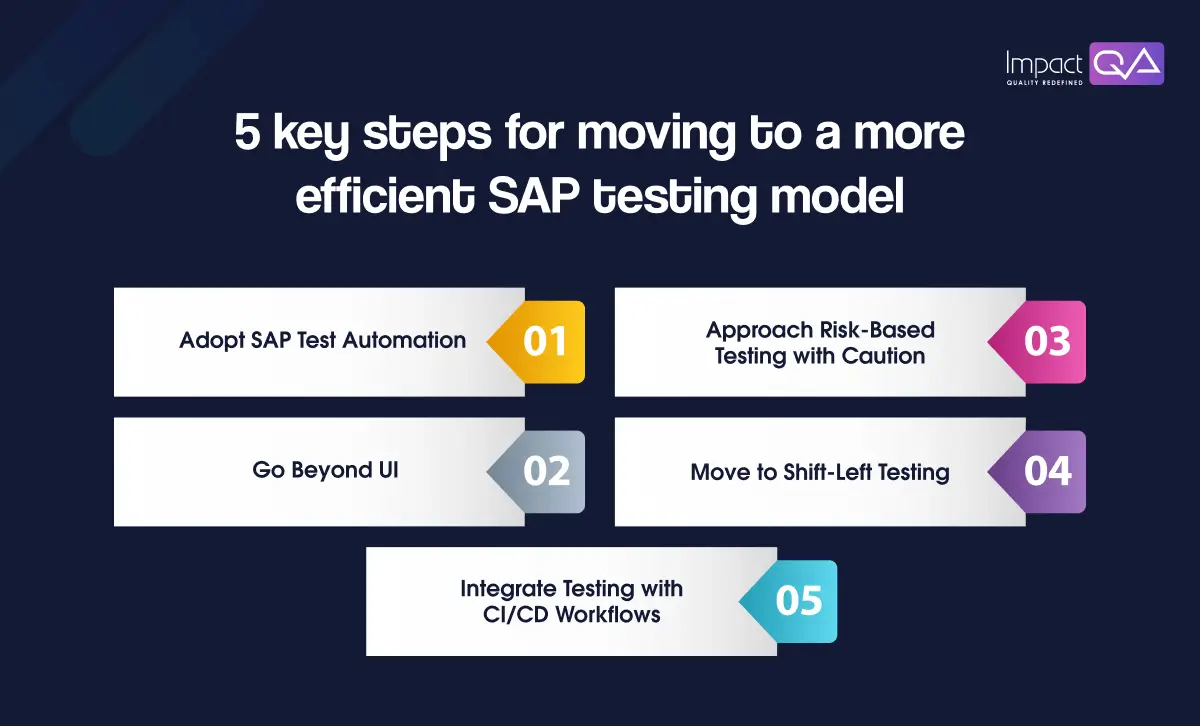
Here are 5 key steps for moving to a more efficient SAP testing model:
1. Adopt SAP Test Automation
Organizations are turning to Robotic Test Automation to safeguard against potential programming bugs, release incompatibilities, and security vulnerabilities. This approach ensures comprehensive testing of every change without relying on manual testing timelines or risking loopholes in critical issue detection. It represents a reinvention of testing practices tailored to the agile demands of modern IT departments.
2. Approach Risk-Based Testing with Caution
The flaw with risk-based testing lies in its focus on scenarios most likely impacted by technical changes in a release. The problem with this form of focused testing methodology is that it often overlooks interconnected scenarios, thus leaving the organization vulnerable to increased risks and potential process delays.
For example, risk-based testing may neglect testing master data, yet even minor changes to master data can profoundly affect business logic and potentially disrupt the system. Therefore, you must approach risk-based testing cautiously and ensure comprehensive coverage to mitigate any overlooked loopholes in the system.
3. Go Beyond UI
Organizations use SAP in various ways, and just testing the UI is like checking the temperature gauge on an engine without looking under the hood. You might know that the engine is cool, but what about the coolant level or the radiator?
Testing must be thorough, covering all aspects, including how other systems and end users are impacted. Manual mapping of how other interfaces are affected by changes in the SAP system is impractical, particularly as the business units rely on other systems to access and use SAP data for crucial functions. A single broken interface, such as with a CRM system, could halt business operations.
4. Move to Shift-Left Testing
Shift-left testing involves conducting early testing and frequently throughout the project lifecycle. As a reality check, most companies often wait till the very end to initiate their SAP testing process, misapprehending it as a complex process with significant dependencies. As a consequence, it often leads to delayed release cycles and defect-ridden products.
By employing service virtualizations, SAP regression testing can begin early in the lifecycle, even before a dedicated QA team is involved. With new testing technologies, organizations are now able to implement shift-left testing more effectively than ever before.
5. Integrate Testing with CI/CD Workflows
The SAP testing shall begin as soon as the code is ready to be deployed. The moment your team reaches the level of testing integrations, going beyond the UI and reaching up to regression testing, you must slip it into the CI/CD workflows. The idea behind incorporating Robotic Test Automation is to streamline the entire testing process and hence incorporating it within the CI/CD workflows can help accelerate the process even further.
Hire Experts to Smoothen the Process
The five key steps mentioned above are only a small part of the key essentials you need to make sure your SAP applications are integrated smoothly into your running business flows. Approaching a professional Software testing solutions provider expert in the SAP testing domain like ImpactQA can help ease out the process.
ImpactQA’s ERP testing solutions offer unique methodologies and a holistic approach to tackle enterprise software testing for every business type. Through their cutting-edge QA services, ImpactQA can provide customized solutions for your end-to-end ERP testing project starting from test planning, strategies, and test preparation to test management, coordination, and implementation.