Core Benefits of Agile Project Management

The pace of change is accelerating, driving a growing demand for projects to be completed swiftly and within tighter budgets. Consequently, traditional lengthy project approaches are becoming obsolete as organizations seek more agile solutions to meet these evolving industry demands. Recent statistics indicate that 71% of organizations use Agile approaches in their Software Development Lifecycle. Additionally, a report by Forbes found that companies adopting Agile methodologies have accelerated software delivery by 64%.
Against this backdrop, Agile Project Management emerges as a strategic imperative for modern businesses. But why is Agile gaining such widespread success, and why do project managers increasingly rely on it either independently or in conjunction with other frameworks? The answer is simple. Through the seamless integration of Agile principles into project management practices, managers attain heightened control over their projects. What sets Agile project management apart is its dual emphasis on delivering both quality and value to the customer while meeting project constraints.
What is Agile Project Management?
Agile Project Management is an approach centered on embracing change throughout the development process. Unlike traditional methods, it prioritizes delivering features with the greatest business value first, while also emphasizing real-time communication to manage project cost, time, and scope effectively.
Traditionally, project managers bear the burden of balancing various aspects such as cost, scope, quality, and risk. However, Agile distributes project responsibilities across three key roles:
- Product Owner: This individual sets project goals, manages scope, adapts to changing requirements, and prioritizes product features.
- Scrum Master: Responsible for guiding the team, prioritizing tasks, and removing obstacles to progress.
- Team Member: Handles task assignments, daily management, quality control, and progress reporting.
Agile streamlines complexity by breaking down the project lifecycle into iterative cycles called “sprints,” typically lasting two to four weeks. Instead of the traditional waterfall approach, where requirements are determined upfront and the product is developed and tested at the end, Agile focuses on delivering small, usable segments of the product in each sprint.
Previously, software development primarily followed the Waterfall model, which lacked the iterative nature of Agile. The Agile approach, however, is iterative and incremental, aimed at facilitating quick delivery of business value. It adheres to the Agile Manifesto principles, emphasizing flexibility, collaborative efforts, continuous improvement, and timely delivery with high quality.
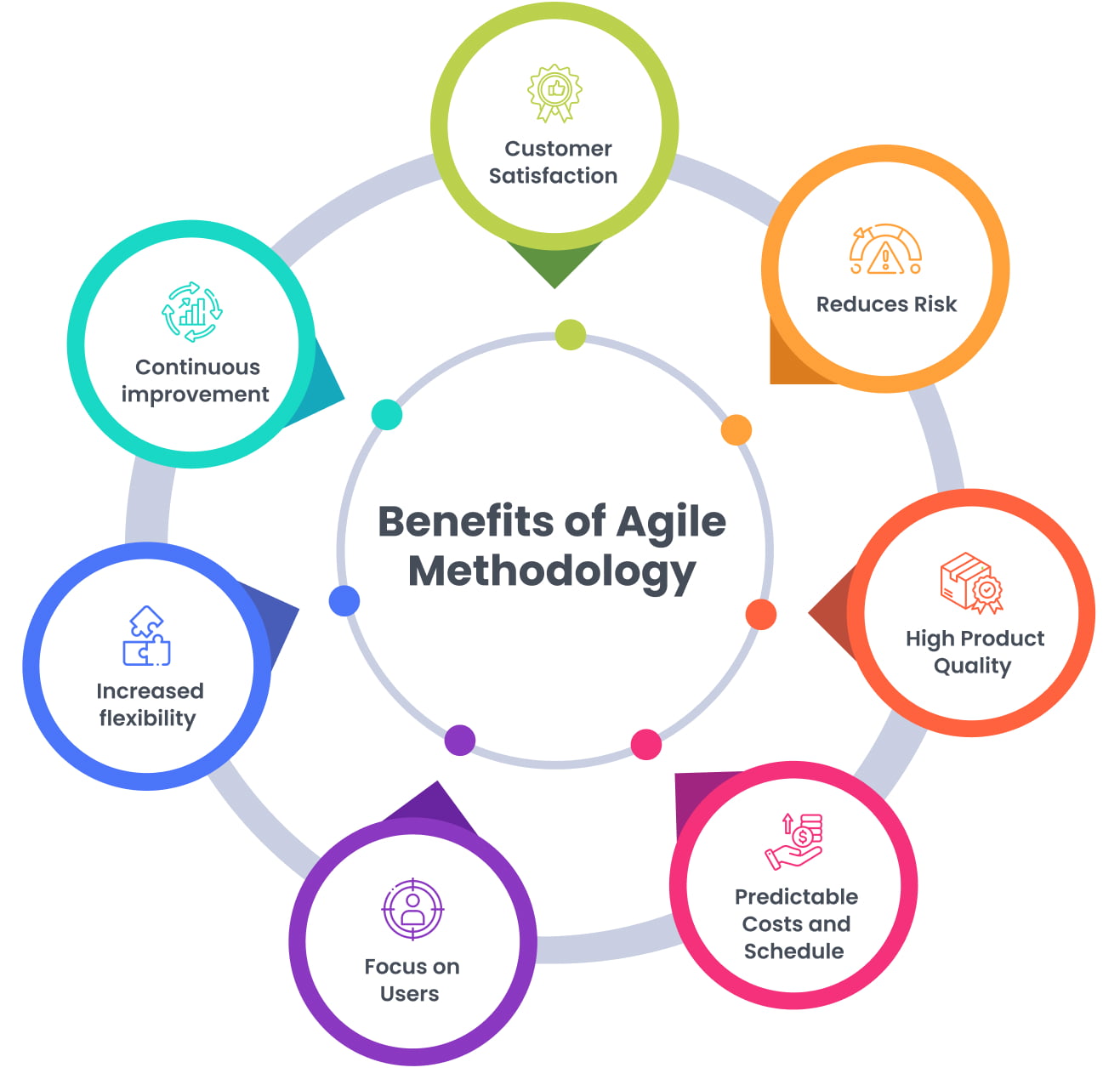
Benefits of Agile Methodology
1. Customer Satisfaction
In Agile methodology, product owners are always involved in the progress of development that is highly visible and flexible to change.
- Customers are involved in the decision-making process which leads to greater customer retention
- Its highest priority is to satisfy the customer through the early and continuous delivery of valuable software.
- Demonstrating working functionalities to customers in every sprint review.
- It delivers products to the market rapidly and frequently with each release.
2. Reduces Risk
Utilizing Agile techniques can reduce the likelihood of project failure, as there is always a working product from the outset of the first sprint, mitigating the risk of future failures.
- Developing in sprints ensures a short time between the initial project investment and validation of the approach.
- Agile provides flexibility when implementing new changes after implementation, with minimal associated costs.
3. High Product Quality
In Agile Methodology, testing is integrated during the cycle, which means that there are continuous checkups to see the product work during development. It also helps the product owner to make changes if needed and the working team is aware if there is an issue in the product.
- It elaborates and defines the requirements just in time so that the knowledge of the product is as relevant as possible to all teams.
- Continuous integration and daily testing into the development process make the development team address that issue at the right time.
- Optimal utilization of automation testing tools is ensured.
- It conducts Sprint retrospectives that allow the scrum team to continuously improve processes and performance.
4. Predictable Costs and Schedule
The product’s cost is predictable and constrained by the team’s capacity within the fixed schedule time box, supplemented by client-provided estimates prior to each sprint.
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
- Working on software over comprehensive documentation.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation.
- Responding to change over plan.
5. Focus on Users
It generally uses user stories with business-focused Acceptance Criteria which define the product features by focusing on the needs of real users, each feature incrementally delivers value. It also provides the opportunity to beta-test software after each sprint.
- All activities are focused on providing tangible business values.
- All activities are focused on providing business value by ensuring a useful, usable, and engaging product.
- The customer is not defined as the project stakeholders, but the end users as well.
6. Increased flexibility
Agile implementation offers unparalleled flexibility to project teams. It enables the teams to work in smaller bursts and incorporate changes rapidly.
- Dividing projects into short sprints allows for manageable and adaptable workflows.
- Constant feedback and involvement of the product owner facilitating quick adjustments to project requirements.
7. Continuous improvement
Agile methodology emphasizes continuous improvement as a core principle. It promotes self-reflection and iterative enhancement.
- Iterative work cycles ensure that each sprint builds upon the previous one, minimizing the repetition of mistakes.
- An open culture of idea exchange and collaboration cultivates shared learning opportunities among team members, thereby enabling collective improvement.
Bottom line
Organizations today seek flexible project delivery methods, gravitating towards Agile Project Management to adapt to rapid changes. While traditional project management processes persist, embracing agility poses perceived risks due to its informality. Yet, a mature Agile approach, coupled with Scrum training, empowers professionals to navigate these challenges, evolving into proficient Scrum Masters who enhance business value.
Agile Project Management stands as a critical strategy for value-driven efficiency amid perpetual flux. Its iterative nature and customer-centric ethos help enterprises address uncertainties, guarantee product excellence, and align with evolving market dynamics.