Cloud ERP VS On-Premise ERP: Which is Right for You?

One of the most critical considerations to make when selecting a new enterprise resource planning (ERP) system for your organization is whether to go with an on-premises ERP system or a cloud-based ERP solution.
Recent statistics highlight the significant shift towards cloud ERP adoption. As of 2024, cloud solutions dominate the market, with nearly all ERP providers offering cloud deployment options. According to research published by GlobeNewswire, the hybrid cloud market is expected to reach USD 173.33 billion by 2025, growing at a robust CAGR of 22.5%.
However, there are reasons why a small or mid-level organization prefers a classic on-premise ERP system over the cloud, which was standard practice in the ERP sector until recently. Factors such as security, scalability, infrastructure requirements, and integration capabilities play important roles in this decision. Each approach presents distinct advantages and challenges, influencing areas from customization flexibility to operational costs.
This blog will explore these crucial considerations to assist businesses in selecting the most appropriate ERP solution aligned with their operational strategies and business objectives.
What is Cloud-Based ERP?
Cloud-based ERP is a software system hosted on remote servers and accessed through the internet. It integrates and manages core business processes such as finance, HR, supply chain, and customer relations in a unified system.
Cloud-based ERP offers several advantages, including lower upfront costs, scalability, and accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. The service provider handles maintenance, updates, and security, freeing businesses from the need to manage their own IT infrastructure.
This model is particularly appealing to small and medium-sized enterprises due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, cloud-based ERP systems can be quickly updated and upgraded. It ensures that businesses have access to the latest features and improvements without significant downtime or resource investment.
What is On-Premise ERP?
On-premise ERP is a software system installed locally on a company’s own servers and computers. It integrates and automates essential business processes such as accounting, procurement, project management, and manufacturing.
On-premises ERP solutions provide high levels of control and customization, which allows businesses to tailor the system to their specific requirements. However, they require significant upfront investment in hardware and software, as well as ongoing maintenance, IT staff, and infrastructure. Security and data control are entirely managed by the business, which can be an advantage for organizations with stringent data protection requirements.
On-premise ERP systems are typically favored by larger enterprises with the necessary resources and in-house expertise to manage the system effectively.
Differentiating Factors for Cloud-based ERP and On-Premise ERP Solutions
These differences can help you decide which ERP system suits your business better.
Aspect |
Cloud-Based ERP |
On-Premise ERP |
|
| 1. | Accessibility and Mobility | Accessible anywhere via an internet connection | Limited access, primarily office-bound |
| 2. | Security of Data | Managed by the provider, may cause concerns | Managed internally, control with the IT team |
| 3. | Integration and Scalability | Easily scalable with flexible integrations | Scalability requires significant hardware investment |
| 4. | Customization and Upgrades | Customizations are maintained during updates | Customizations need re-implementation after upgrades. |
| 5. | Total Cost of Ownership | Lower upfront cost, continuous expenses | High initial cost, ongoing improvement fees |
Accessibility and Mobility
The mobility and flexibility inherent in cloud-based ERP software are highly appealing. Data stored in these systems is readily accessible from anywhere and at any time, using any device connected to the internet. This empowers the companies with increased visibility and control over their operations.
This flexibility is lacking in on-premise ERP systems, which offer limited remote access and often prevent you from overseeing business operations when you are not in your office.
Security of Data
Data security is a major concern for businesses and plays an important role in choosing which software to implement.
With cloud ERP solutions, your business data is managed by the service provider. Despite their stringent security measures, some firms are uneasy as they lack complete control. According to a BT survey, 49 percent of IT decision-makers are extremely concerned about the security of cloud services.
On-premises ERP, on the other hand, places data security in the hands of your in-house IT team, which can sometimes be counterproductive. Your security measures may not be as robust as desired, making you more vulnerable if you rely solely on internal resources instead of a well-established service provider.
While an on-premise ERP solution consolidates your information into a centralized and secure server network, selecting a professional partner with a cloud-based system ensures their security measures are adequate for protecting your sensitive data. To minimize security breaches, cloud ERP systems host their client data in multiple locations on the web.
Integration and Scalability
Scalability relates to an ERP system’s ability to handle an increased volume of data and users as your company grows.
A cloud ERP system provides this flexibility and allows for significant integration, enabling it to function well even as the workload increases. While an on-premise ERP solution can help your firm grow. You will need to invest in additional hardware deployment costs to achieve that growth.
Customization and Upgrades
On-premise ERP software permits users to customize their software, integrating these modifications directly into the existing program. This means that if your provider releases an upgrade, you’ll need to re-implement those changes, which can be challenging.
When you choose an on-premise ERP solution, your IT personnel will be expected to administer and maintain your software continuously and have a solid plan to modify your data-related hardware, contracts, and licensing.
Cloud-based ERP can help your company avoid these inconvenient, stressful, and time-consuming procedures.
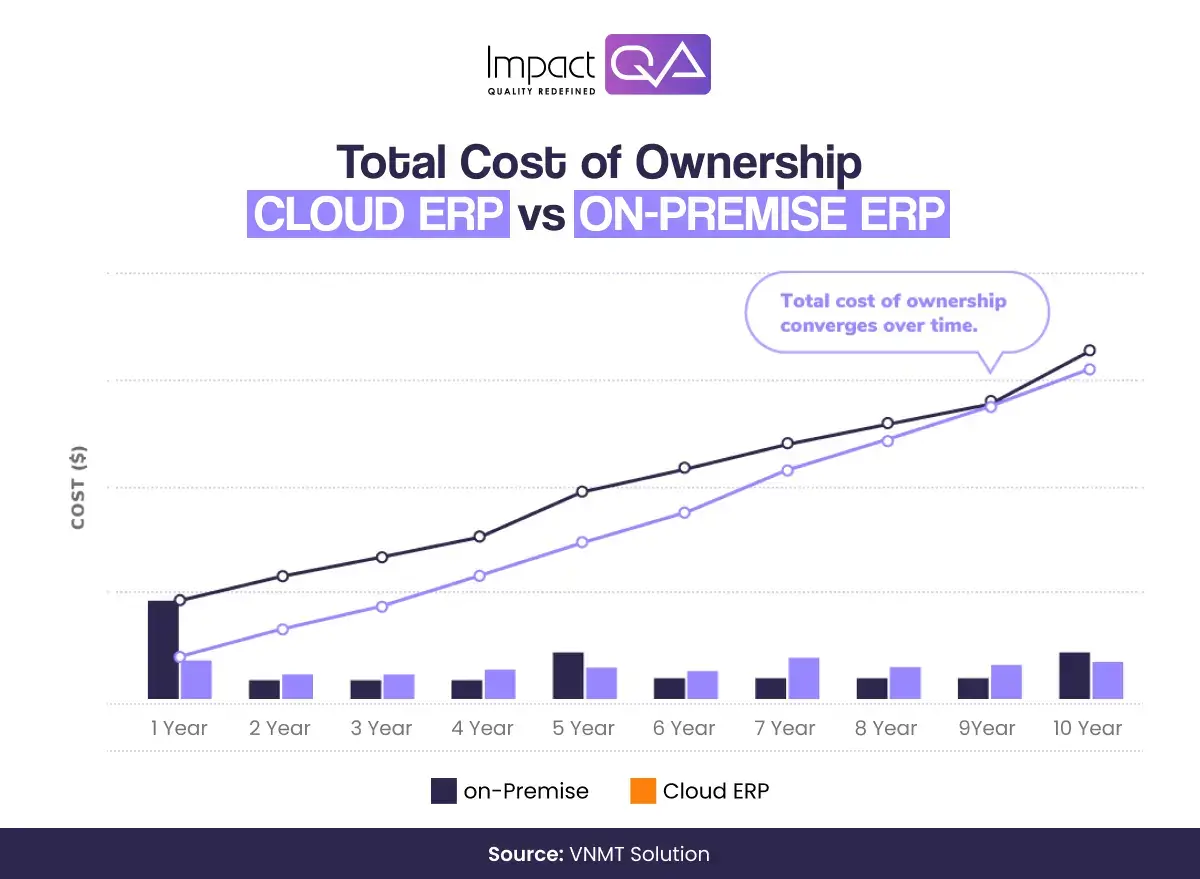
Total Cost of Ownership and Deployment
Every ERP deployment, regardless of type, requires time and careful planning. However, the cost and time involved may differ depending on your choice.
On-premise ERP systems demand a significant upfront investment in hardware, licenses, and infrastructure. Although ongoing maintenance costs are lower, businesses must allocate budget for internal IT resources, system updates, and hardware upgrades. These factors result in higher long-term ownership costs, making it a more expensive option over time.
In contrast, cloud solutions have a lower upfront fee but incur ongoing costs. According to an Oracle analysis, cloud applications consume 91 percent less energy than their on-premise counterparts, which is beneficial for those concerned about their carbon footprint.
The high cost of on-premises ERP often inhibits small and medium-sized firms, who historically prefer cloud-based ERP to distribute costs more evenly across the product’s lifecycle. The low entry cost necessary to implement cloud-based ERP software is one reason why 93 percent of businesses have chosen this option. Nevertheless, system costs tend to converge over time.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Cloud-ERP
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Cloud-ERP systems often raise data security and privacy concerns. Since data is stored off-site and managed by third-party providers, organizations may worry about unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance with regulations.
Limited Customization and Control
While cloud-ERP solutions are generally more flexible, they often offer fewer customization options compared to on-premise systems. Organizations with unique or complex requirements might find cloud options restrictive, as they may not allow for the level of customization needed to tailor the system to specific business processes.
Dependence on Internet Connectivity
Cloud-ERP systems require a reliable internet connection for access and functionality. Any disruption in internet service can lead to significant downtime, affecting business operations. This dependency can be a critical drawback, especially for businesses in areas with unstable internet connectivity.
Subscription Costs and Long-Term Expenses
Although cloud-ERP solutions can be cost-effective initially due to lower upfront costs, the subscription model can become expensive over time. Continuous subscription fees, along with potential costs for additional features and services, can add up, making the total cost of ownership high in the long run.
Data Migration and Integration Challenges
Migrating existing data to a cloud-ERP system can be complex and time-consuming. Integration with other on-premise or third-party systems might also present challenges. It might require careful planning and possibly additional investment in integration tools and services.
Challenges and Drawbacks of On-Premise ERP
High Initial Costs and Ongoing Maintenance
On-premise ERP systems generally require substantial initial investments in hardware, software, and infrastructure. Additionally, maintaining these systems requires ongoing expenditures for updates, security patches, and hardware replacements, leading to high total costs of ownership.
Long Implementation Times
Implementing an on-premise ERP system is often a lengthy process, involving extensive planning, customization, and testing. This can lead to delays in realizing the benefits of the ERP system and may disrupt regular business operations during the transition period.
Limited Remote Access
Accessing on-premise ERP systems remotely can be difficult and less efficient compared to cloud solutions. Businesses that require mobile access or support for remote work might find on-premise solutions limited, as setting up secure remote access can be complex and costly.
Resource-Intensive Management
Managing an on-premise ERP system demands significant internal IT resources. Organizations need dedicated staff for system administration, troubleshooting, and ensuring optimal performance. This can divert resources from other critical IT projects and initiatives.
Upgrades and Compatibility Issues
Upgrading an on-premise ERP system can be cumbersome and disruptive. Businesses may face compatibility issues with other systems and customizations during upgrades, necessitating additional time and resources to resolve these challenges. This can result in prolonged downtime and impact business continuity.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct ERP system for your company may be difficult since there is no one-size-fits-all ERP solution. Both on-premises and cloud ERP software have their own advantages and disadvantages. Rather than forcing contemporary technology, the decision to choose the best ERP software for your company should be based on what helps the business the most.